
AMD FidelityFX™ Brixelizer/GI
AMD FidelityFX™ Brixelizer GI is compute-based real-time dynamic global illumination solution built upon sparse distance fields.
GeometryFX improves the rasterizer efficiency by culling triangles that do not contribute to the output in a pre-pass. This allows the full chip to be used to process geometry, and ensures that the rasterizer only processes triangles that are visible.
GeometryFX with RDNA
GeometryFX with RDNA GeometryFX was primarily designed for GCN-architecture GPUs. Developers are encouraged to measure results on RDNA and only enable GeometryFX if gains are observed.
GeometryFX improves the rasterizer efficiency by culling triangles that do not contribute to the output in a pre-pass. This allows the full chip to be used to process geometry, and ensures that the rasterizer only processes triangles that are visible.
A good use case for the GeometryFX library is depth-only rendering of opaque geometry – for example, in shadow maps:
At its core, GeometryFX works by generating an intermediate index buffer which consists of visible triangles only. Intermediate buffers are reused as much as possible to minimize memory usage. GeometryFX also buffers up draw calls to execute the filtering on one batch while the previous batch is being rendered, allowing the filtering to overlap with the actual draw call.
The library makes heavy use of multi-draw-indirect. This is a D3D11 driver extension exposed through the AMD GPU Services (AGS) library. It allows multiple draw calls to be prepared on the GPU and executed with a single API call.
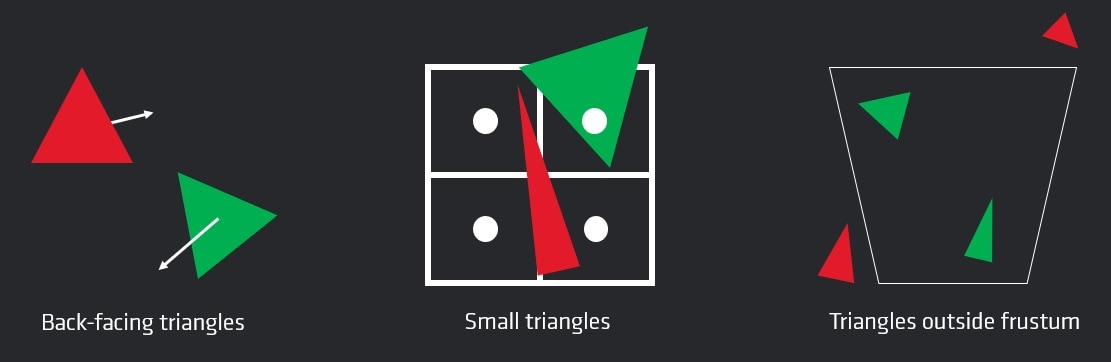
GeometryFX processes your triangles in compute, and looks for triangles that don’t ultimately contribute to the scene.