Download the latest version - v1.1.4
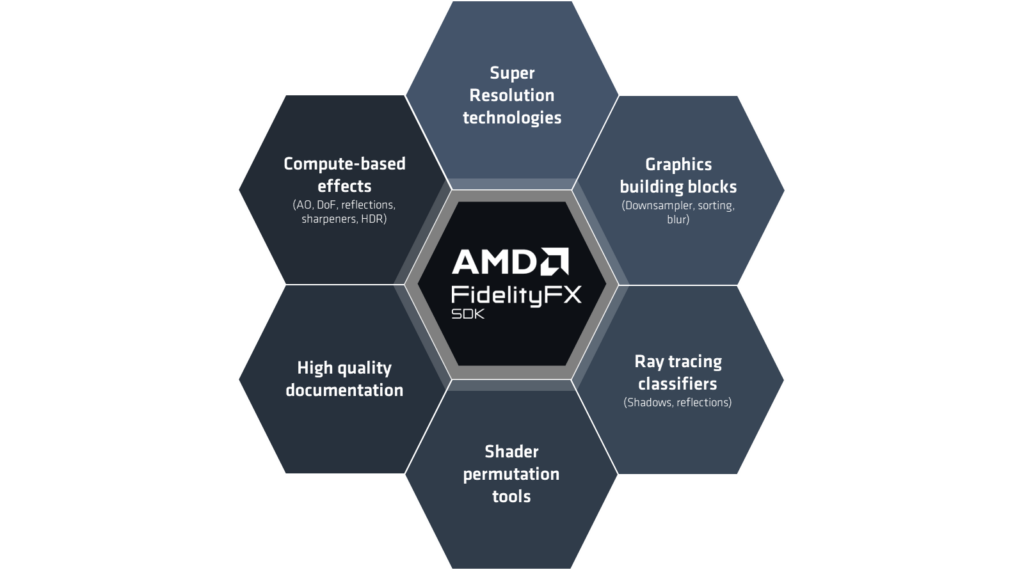
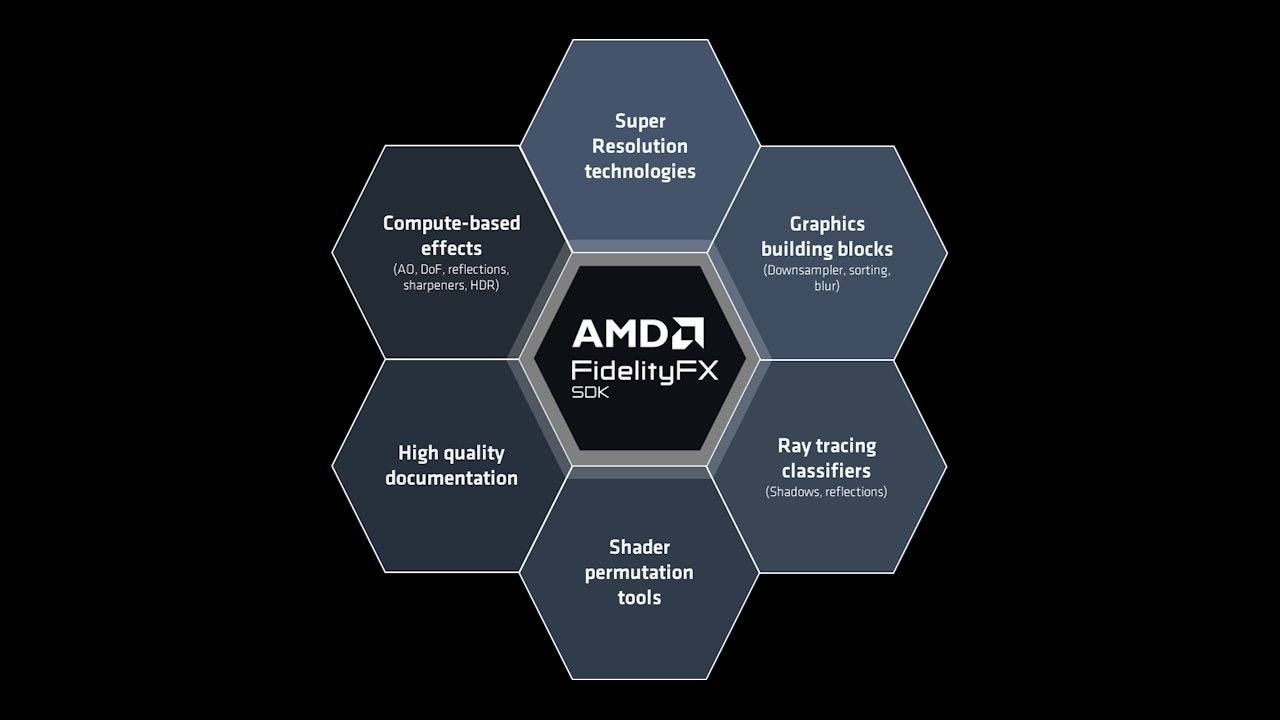
This release of the AMD FidelityFX™ SDK adds the following features:
- Additions to the API and fixes for issues discovered.
Features
State-of-the-art algorithm
Optimized for Shader Model 6.0+
Open source, MIT license
Additional features:
- Direct and Indirect execution support.
- AMD RDNA™ architecture and above optimized algorithm.
- 32-bit key and payload sort support
- Support for DirectX® 12 API and Vulkan®.
- Shaders written in HLSL utilizing Shader Model 6.0 wave-level operations.
A sample application is provided for DirectX® 12 and Vulkan®.
Details
Algorithm overview
AMD FidelityFX™ Parallel Sort is an AMD RDNA™ architecture-optimized version of the Radix Sort algorithm.
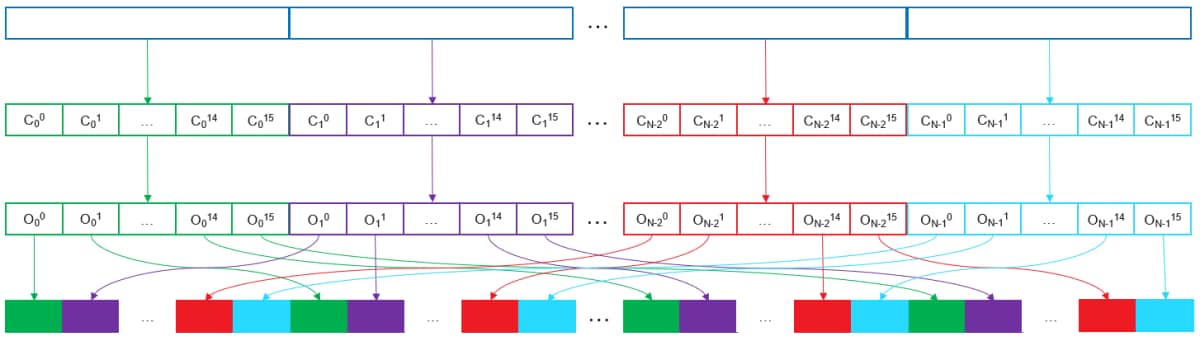
At a high level, the algorithm works by recursing over a data set to be sorted (key or key/value pairs), and re-arranging it in place by 4-bit increments. Each pass guarantees that the data set is fully sorted up to the number of bits processed. For example, after 4 iterations, we are guaranteed that the first 16 bits of the key is properly sorted.
For each iteration that is executed, 5 actions are taken on the data set:
- The 4-bit value range we are currently sorting is summed up into buckets from 0-15, so that we know how many of each value occurs throughout the data set.
- The number of occurrences go through a reduction phase in order to pre-increment offsets on a thread group basis later on.
- The reduced occurrences go through a scan-prefix to calculate offset values for each value group (0-15) on a thread group basis.
- The full occurrences buffer then also goes through a scan-prefix, and adds the reduced scan-prefix values to properly index the data across all thread groups.
- The data set is read in one more time, and written to its new sorted offset location. If there is also a payload, it is also copied over at this time.
Once all iterations have run (in the case of 32-bit keys, it runs 8 times), the entire data set is sorted.
Developer Testimonials

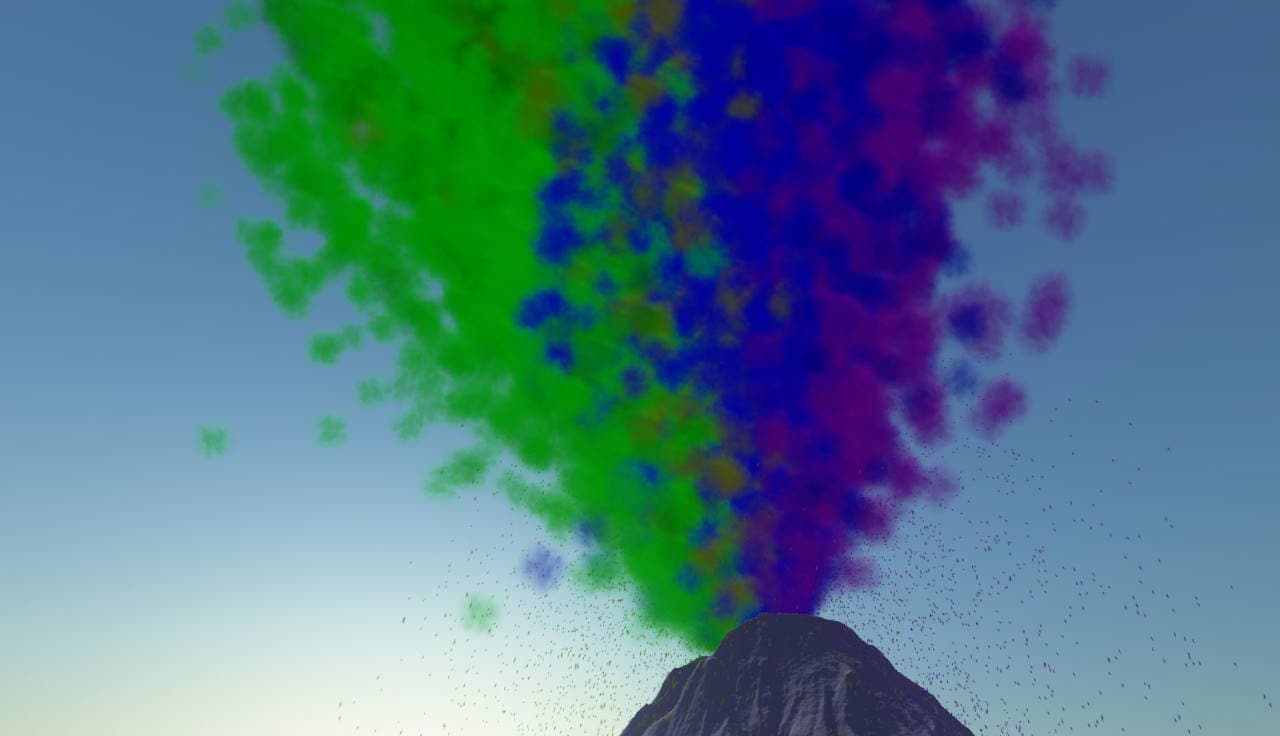
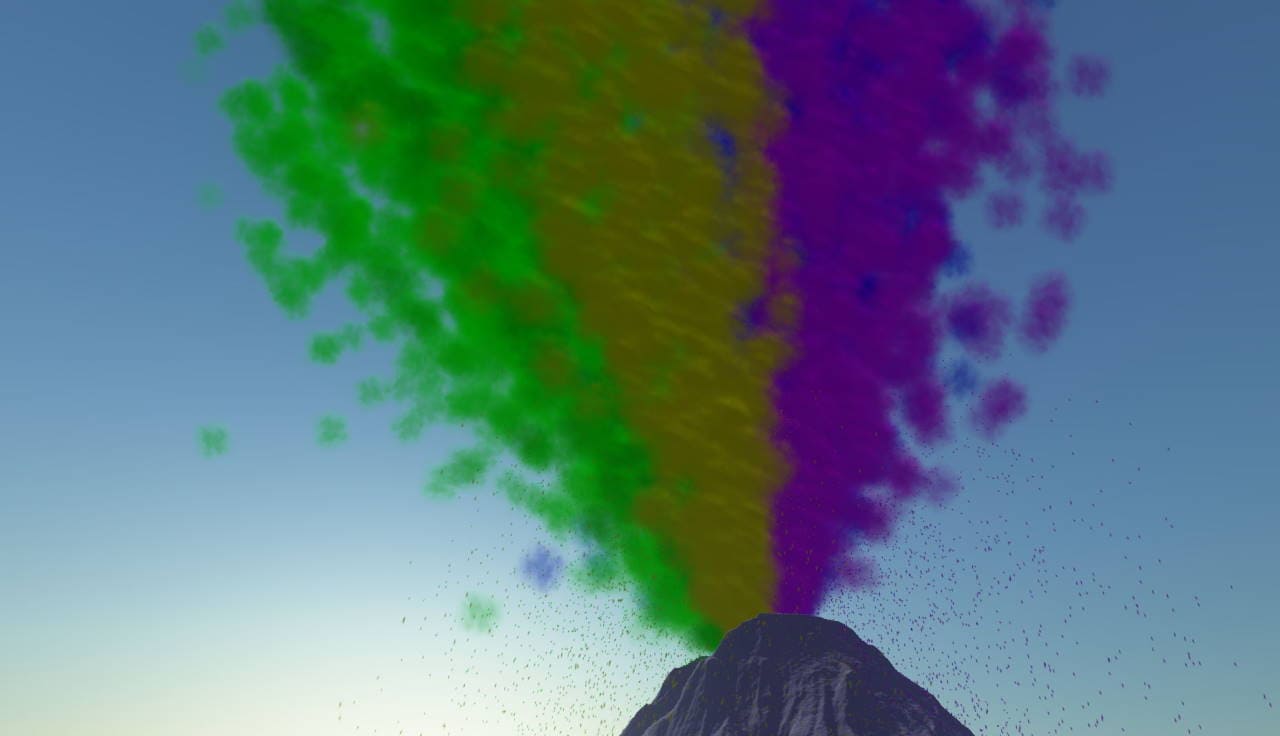
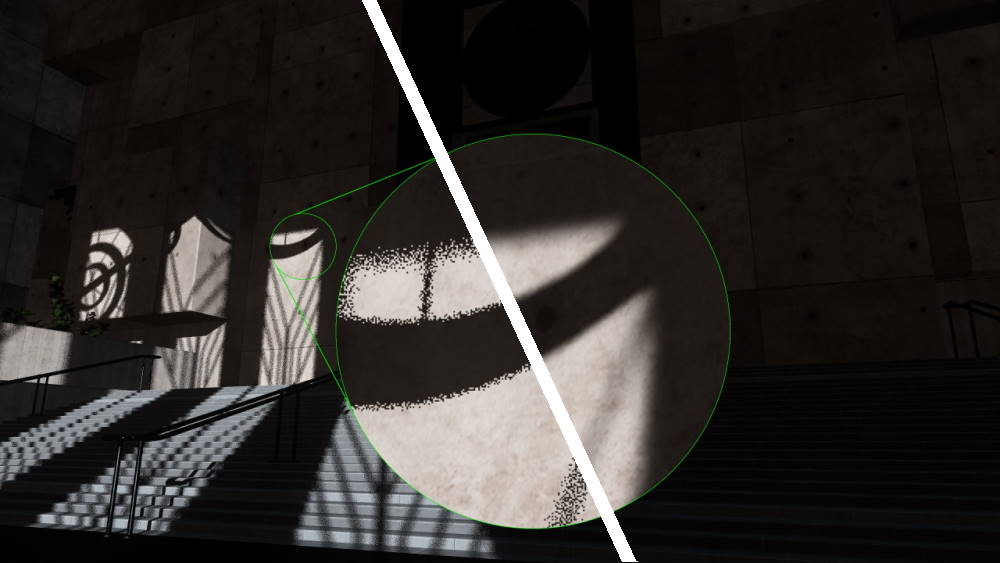
Comparison: GPU particle sorting
Comparison: image index buffer sorting
Requirements
- DirectX® 12
- Vulkan®