HIP Threads: GPU power for teams without GPU experts
HIP Threads lets C++ teams eliminate CPU hotspots by running familiar multithreaded code on AMD GPUs, no kernel rewrites or GPU expertise required, delivering real speedups in days.
If you’re interested in deploying advanced AI models on your local hardware, leveraging a modern AMD GPU or APU can provide an efficient and scalable solution. You don’t need dedicated AI infrastructure to experiment with Large Language Model (LLMs); a capable Microsoft® Windows® PC with PyTorch installed and equipped with a recent AMD graphics card is all you need.
PyTorch for AMD on Windows and Linux is now available as a public preview. You can now use native PyTorch for AI inference on AMD Radeon™ RX 7000 and 9000 series GPUs and select AMD Ryzen™ AI 300 and AI Max APUs, enabling seamless AI workload execution on AMD hardware in Windows without any need for workarounds or dual-boot configurations. If you are new and just getting started with AMD ROCm™, be sure to check out our getting started guides here.
This guide is designed for developers seeking to set up, configure, and execute LLMs locally on a Windows PC using PyTorch with an AMD GPU or APU. No previous experience with PyTorch or deep learning frameworks is needed.
| AMD Radeon™ AI PRO R9700 | AMD Radeon™ RX 7900 XTX | AMD Radeon™ PRO W7900 | AMD Ryzen™ AI Max+ 395 |
| AMD Radeon™ RX 9070 XT | AMD Radeon™ PRO W7900 Dual Slot | AMD Ryzen™ AI Max 390 | |
| AMD Radeon™ RX 9070 | AMD Ryzen™ AI Max 385 | ||
| AMD Radeon™ RX 9060 XT | AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 HX 375 | ||
| AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 HX 370 | |||
| AMD Ryzen™ AI 9 365 |
OS Supported: Microsoft® Windows® 11
AMD Software: PyTorch on Windows Preview Edition 25.20.01.14 driver
Python 3.12 - Python Release Python 3.12.0 | Python.org
First, we need to open the Command Prompt
cmd, and press Enter. A black terminal window will pop up.
A “virtual environment” is like a clean, empty sandbox for a Python project.
In your Command Prompt, type the following command and press Enter. This
creates a new folder named llm-pyt that will house our project.
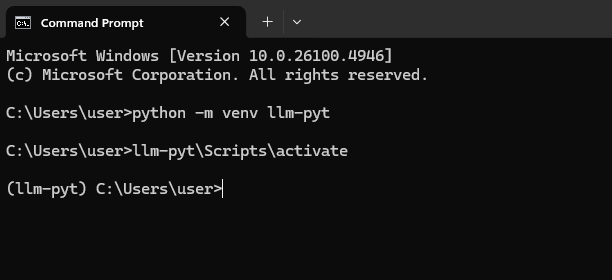
python -m venv llm-pyt
Next, we need to “activate” this environment. Think of this as stepping inside the sandbox.
llm-pyt\Scripts\activate
You’ll know it worked because you’ll see (llm-pyt) appear at the beginning of your command line prompt.
Now we’ll install the software libraries that do the heavy lifting. The most important one is PyTorch, an open-source framework for building and running AI models. We need a special version of PyTorch built to work with AMD’s ROCm technology.
We will also install Transformers and Accelerate, two libraries from Hugging Face that make it incredibly easy to download and run state-of-the-art AI models.
Run the following command in your activated Command Prompt. This command
tells Python’s package installer (pip) to download and install
PyTorch for ROCm, along with the other necessary tools.
pip install --no-cache-dir https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/windows/rocm-rel-6.4.4/torch-2.8.0a0%2Bgitfc14c65-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whlpip install --no-cache-dir https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/windows/rocm-rel-6.4.4/torchaudio-2.6.0a0%2B1a8f621-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whlpip install --no-cache-dir https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/windows/rocm-rel-6.4.4/torchvision-0.24.0a0%2Bc85f008-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whlpip install transformers accelerateThe moment of truth. Let’s give our new setup a task: running a small but powerful language model called Llama 3.2 1B.
Make sure your Command Prompt still has the (llm-pyt) environment
active. If you closed it, just re-open cmd and run llm-pyt\Scripts\activate.
Now, start Python:
pythonCopy the entire code block below. Paste it into your Python terminal (where you see the >>>) and press Enter.
The first time you do this, it will download the model (which is a few gigabytes), so it may take several minutes. Subsequent runs will be much faster.
import torchfrom transformers import pipelinemodel_id = "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct"pipe = pipeline( "text-generation", model=model_id, dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")pipe("The key to life is")You should see an output similar to this:
[{'generated_text': 'The key to life is not to get what you want, but to give what you have.The best way to make life more meaningful is to practice gratitude, and to cultivate a senseof contentment with what you have. If you want to make life more interesting, you must bewilling to take risks, and to embrace the unknown. The best way to avoid disappointment isto be patient and persistent, and to trust in the process. By following these principles,you can live a more fulfilling life, and make the most of the time you have.'}]You can return to your command prompt by typing exit() and pressing
Enter.
exit()Running a single prompt is fun, but a real conversation is better. In this section, we’ll create an interactive chat loop that “remembers” the conversation, allowing you to have a back-and-forth with the AI.
Open a new file in your text editor.
Copy and paste the chatbot code below.
import torchfrom transformers import pipeline
print("Loading chat model...")
model_id = "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct"pipe = pipeline( "text-generation", model=model_id, dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto",)
# This list will store our conversation historymessages = []
print("\nChatbot ready! Type 'quit' or 'exit' to end the conversation.")print("-" * 20)
while True: # Get input from the user user_input = input("You: ")
# Check if the user wants to exit if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit"]: print("Chat session ended.") break
# Add the user's message to the conversation history messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
# Generate the AI's response using the full conversation history outputs = pipe(messages, max_new_tokens=500, do_sample=True, temperature=0.7)
# The pipeline returns the full conversation. The last message is the new one. assistant_response = outputs[0]['generated_text'][-1]['content']
# Add the AI's response to our history messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_response})
# Print just the AI's new response print(f"AI: {assistant_response}")run_chat.py in the same user folder.Step 2: Run your chatbot
In your Command Prompt, run the new script:
python run_chat.pyThe terminal will now prompt you with You:. Type a question and press Enter. The AI will respond, and you can ask follow-up questions. The chatbot will remember the context of the conversation.
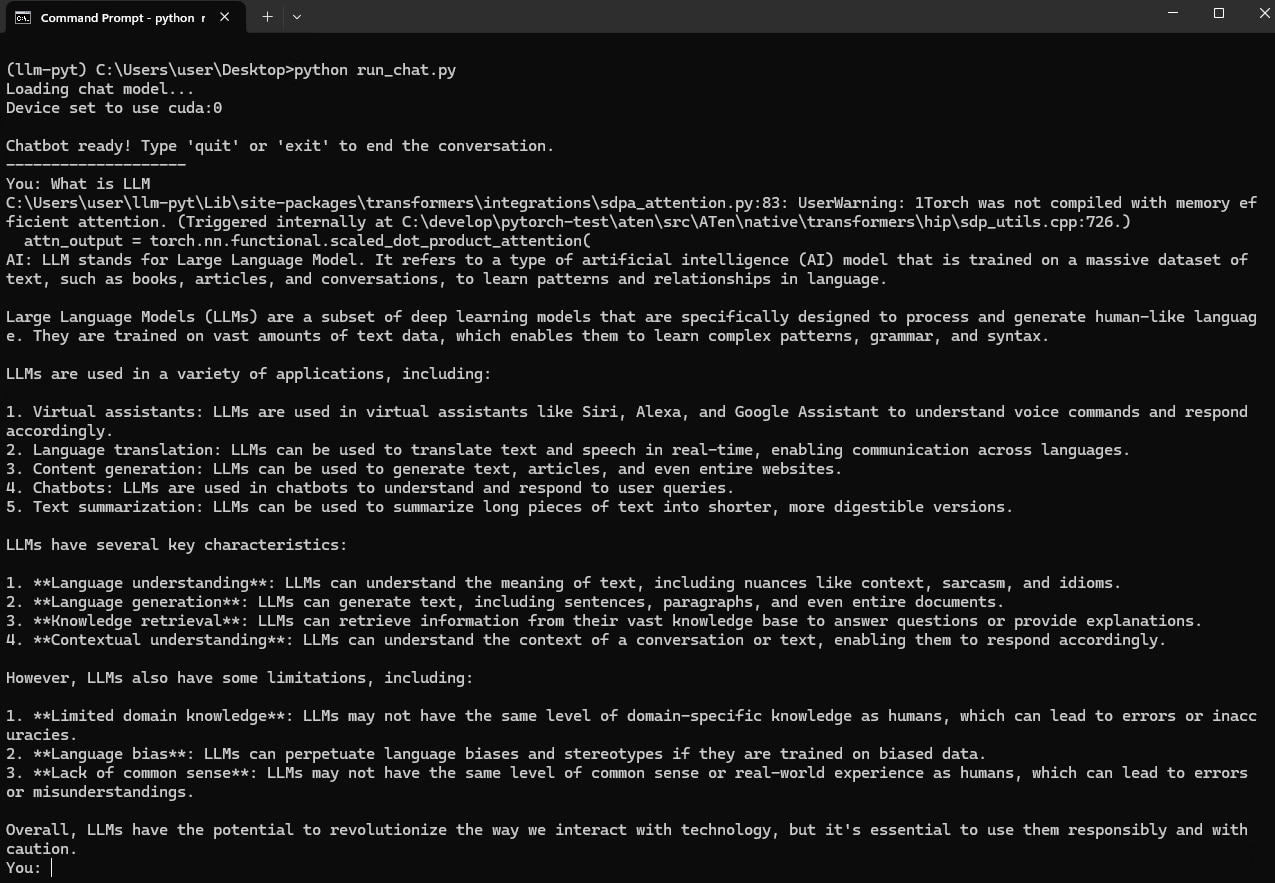
Note:
When you run the LLM, you will see a warning message like this:
UserWarning: 1Torch was not compiled with memory efficient attention.(Triggered internally at C:\develop\pytorch-test\aten\src\ATen\native\transformers\hip\sdp_utils.cpp:726.)Don’t worry, this is expected, and your code is working correctly!
What it means in simple terms: PyTorch 2.0+ introduced a feature called “Memory-Efficient Attention” to speed things up. The current version of PyTorch for AMD on Windows doesn’t include this specific optimization out-of-the-box. When PyTorch can’t find it, it prints this warning and automatically falls back to the standard, reliable method.
By following this blog, you should be able to get started with running transformer-based LLMs with PyTorch on Windows using AMD consumer graphics hardware.
You can learn more about our road to AMD ROCm on Radeon for Windows and Linux in the blog from Andrej Zdravkovic, SVP and AMD Chief Software Officer, here.
View endnotes
PyTorch, the PyTorch logo and any related marks are trademarks of The Linux Foundation.
Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft group of companies.