AMD Radeon™ Developer Panel
The RDP provides a communication channel with the Radeon™ Adrenalin driver. It generates event timing data used by the Radeon™ GPU Profiler (RGP), and the memory usage data used by the Radeon™ Memory Visualizer (RMV).
We are excited to announce the latest release of the AMD Radeon™ Developer Tool Suite (RDTS). RDTS continues to evolve, providing developers with cutting-edge tools to optimize and analyze their applications on AMD hardware. With each release, we aim to deliver features that address the needs of modern GPU workloads. This release includes updates to several key components, each bringing new features and enhancements to improve your development workflow.
This release extends support to the latest AMD hardware, including the AMD Radeon™ RX 9060 graphics card and the AMD Ryzen™ AI 5 330 processor, featuring AMD Radeon™ 820M Graphics. These additions ensure that developers can leverage the full capabilities of the newest AMD architectures. Some features in this new update to RDTS require AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition™ 25.10.2 or higher. We always recommend using the latest Adrenalin Edition release with RDTS.
With the introduction of AMD Radeon™ Software for Linux® version 25.20-based drivers, the AMDVLK driver is no longer included in the amdgpu-pro driver package. This is a result of the AMDVLK open-source project being discontinued as mentioned here. Instead, the RADV open-source Vulkan® driver is installed by default. Consequently, the AMD Radeon™ Developer Panel (RDP) does not support capturing data from Vulkan applications when using these newer driver releases. To analyze Linux Vulkan workloads with AMD Radeon™ GPU Profiler (RGP), AMD Radeon™ Raytracing Analyzer (RRA), or AMD Radeon™ Memory Visualizer (RMV), users can opt for an AMD Radeon™ Software for Linux® version 25.10-based driver. Alternatively, analysis can be performed using the data capture mechanism integrated within the RADV driver, although this method is not supported by RDP. For more information on configuring RADV, refer to the environment variable documentation, specifically the MESA_VK_TRACE_* environment variables which can be utilized for enabling and configuring tracing.
Below, you can find details for new features introduced by each tool for this release.
We’re excited to announce the release of AMD Radeon™ GPU Profiler (RGP) 2.6, which brings significant enhancements to the capture and visualization of performance counters, providing deeper insights into GPU workloads. This version introduces several new memory-related counters, expanding the tool’s capabilities to offer more detailed profiling data for developers.
One of the first things you might notice after capturing a new profile with this release and loading that profile into RGP is that there are more performance counters shown in the Wavefront occupancy pane.
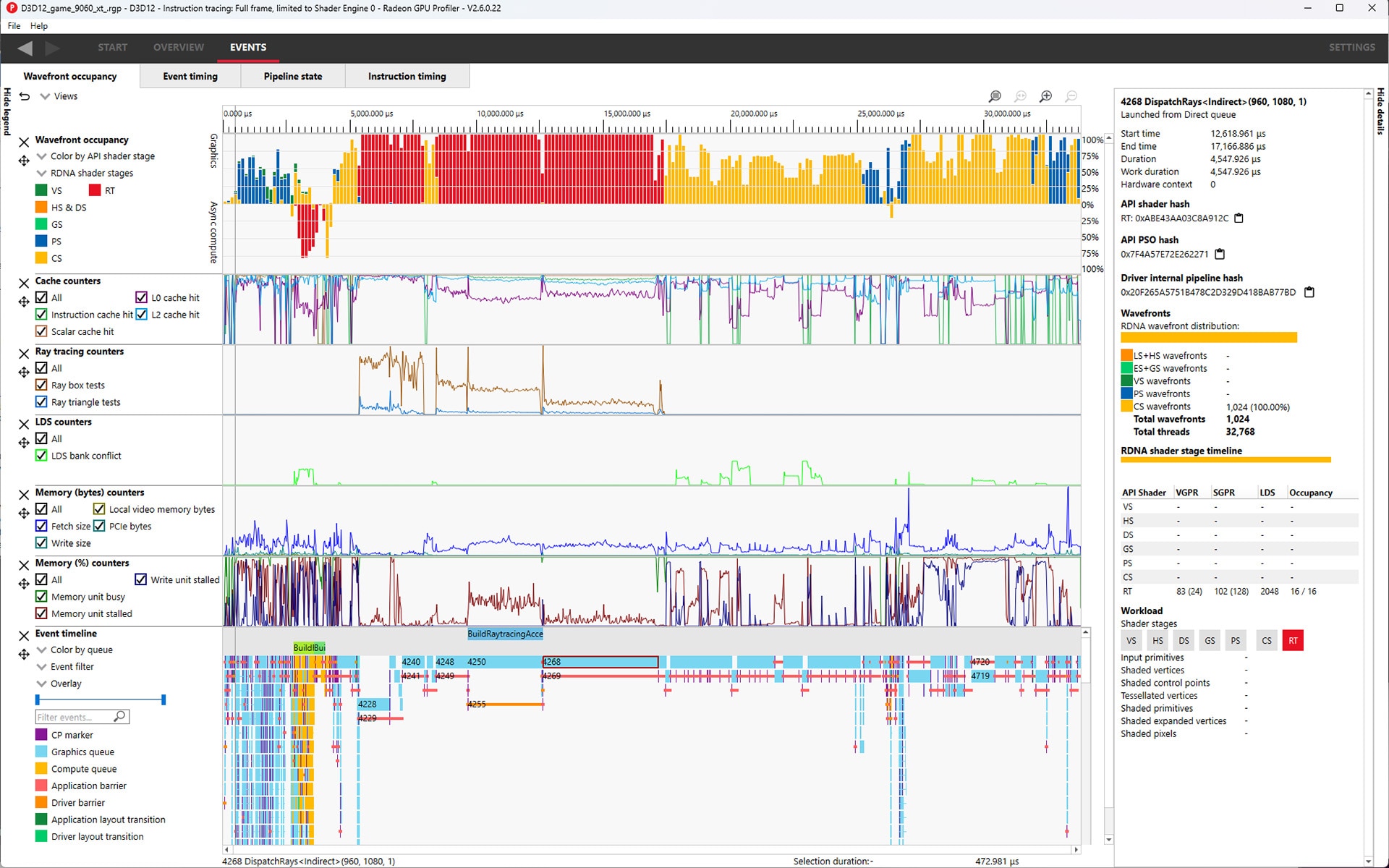
As you can see, this release now captures and visualizes additional memory-related counters, available for workloads executing on GPUs based on AMD RDNA™ 3 and AMD RDNA 4 architectures, as well as APUs based on AMD RDNA 3.5 architecture. These new counters, which are visible as new rows in the Wavefront occupancy pane, are categorized into three groups:
LDS Counters: When profiling compute workloads with local data store
(LDS) bank conflicts, RGP now displays LDS bank conflict counter values,
providing insights into the percentage of GPU time stalled by bank conflicts.
The effect that LDS bank conflicts can have on overall performance is
described well in this excellent article on optimizing a matrix
mulitplication workload.

Memory (Bytes) Counters: This section visualizes value-based memory counter
data, including fetch size, write size, local video memory bytes, and PCIe
bytes. These counters help developers understand the total bytes fetched and
written to video memory, including any cache or memory effects.

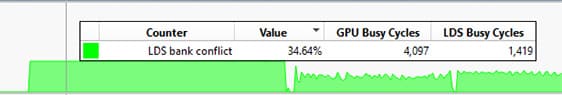
Memory (%) Counters: This section visualizes percentage-based memory
counter data, such as memory unit busy, memory unit stalled, and write unit
stalled. These counters provide insights into the percentage of GPU time the
memory unit is active or stalled, helping developers optimize fetches and
writes.

Additionally, tooltips in the LDS and Memory (%) graphs now show extra columns for GPU Busy Cycles and associated busy cycles, offering more context for performance analysis.
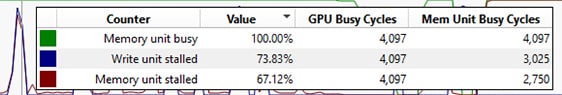
Dynamic VGPR (Vector General Purpose Register) allocation in the AMD RDNA 4 architecture allows the GPU to allocate registers dynamically based on the needs of the workload, rather than pre-allocating a fixed number of registers. This flexibility can lead to more efficient use of GPU resources, as it allows for better optimization of register usage across different shader programs. By dynamically adjusting the number of VGPRs, the GPU can potentially reduce register pressure, leading to improved performance and efficiency in executing complex shaders. This feature is currently primarily used in raytracing pipelines, but could be applied to additional shader types in the future.
RGP 2.6 introduces a new UI element in the Pipeline state pane that indicates whether or not a shader makes use of dynamic VGPR allocation. This enhancement allows developers to quickly identify shaders using dynamic VGPR allocation.
The latest release of AMD Radeon™ GPU Detective, RGD 1.6, introduces a powerful new feature: Shader Resource Descriptor (SRD) Analysis. This enhancement is designed to assist developers in diagnosing complex page fault GPU crash cases.
In RGD 1.6, when an offending or in-flight instruction utilizes an SRD such as an image, buffer, sampler, or BVH, the tool will decode the SRD, disassemble it and present the information in the output file in a new “Shader Resource Descriptor (SRD) analysis” subsection, under the SHADER INFO section.
This feature can be helpful in diagnosing issues like stale, corrupted, or incorrectly indexed descriptors, which often manifest as page faults or invalid memory access.
Examples of the details you may find in the SRD analysis output include address, format and dimensions for image resources, LOD biases for sampler resources and many more.
Note that the SRD analysis feature requires SGPR/VGPR register collection to be enabled at capture time. Since SGPR/VGPR collection increases the crash dump (.rgd) file size, this option is not enabled by default in the AMD Radeon Developer Panel (RDP). You can easily enable this option through the RDP UI before starting any Crash Analysis session if necessary.
The latest update to the AMD Radeon™ Raytracing Analyzer, RRA 1.10, brings improvements that enhance usability and accuracy in raytracing analysis.
In RRA 1.10, the BLAS/TLAS viewer tree views have been updated to improve clarity and usability. Checkboxes for disabled nodes are now automatically unchecked, providing a more intuitive and cleaner interface for developers navigating complex raytracing structures.
RRA 1.10 also addresses an important accuracy issue by fixing the triangle area calculation for very small triangles. This improvement ensures that developers receive precise data when analyzing raytracing workloads, particularly in scenarios involving intricate geometries.
The new release of AMD Radeon™ Memory Visualizer, RMV 1.14, introduces an enhancement aimed at improving the visualization and analysis of memory usage in GPU applications.
RMV 1.14 now includes UI support for work graph backing memory. This feature provides developers with a more comprehensive view of how memory is allocated and utilized within work graphs, enabling more effective optimization and debugging of memory-related issues. By visualizing the backing memory, developers can gain insights into memory usage patterns and identify potential areas for improvement in their applications.
The latest version of AMD Radeon™ GPU Analyzer, RGA 2.14, expands its support to include the AMD Instinct™ MI350 Series GPUs, providing developers with the tools they need to optimize and analyze their applications on this advanced hardware. This update ensures that developers can leverage the full capabilities of the AMD Instinct™ MI350 Series GPUs, enhancing performance and efficiency in their GPU workloads.
The latest update to the AMD Radeon™ Developer Panel, RDP 3.4, introduces features related to the new capabilities of RGP and RGD, providing developers with more comprehensive profiling and debugging tools.
RDP 3.4 now supports collecting the additional memory related counters mentioned above for profiles captured on AMD RDNA 3 and RDNA 4 architecture-based hardware. This enhancement aligns with the new features in RGP 2.6, offering developers deeper insights into memory usage and performance bottlenecks in their applications.
In conjunction with the new Shader Resource Descriptor (SRD) Analysis feature in RGD 1.6, RDP 3.4 adds support for capturing wave SGPRs and VGPRs in crash dumps. This feature provides more detailed information about the resource descriptors used by an in-flight instruction at the time of a crash, aiding developers in diagnosing and resolving issues more effectively.
We are thrilled to bring you these updates in the AMD Radeon Developer Tool Suite, designed to empower developers with enhanced capabilities for profiling, analyzing, and optimizing their GPU applications. To learn more about these tools and download the latest release, visit AMD GPUOpen Tools and explore the full suite of developer tools and resources available to support your development journey.
Vulkan® is the registered trademark of the Khronos Group Inc.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
