
Training an X-ARM 5 robotic arm with AMD Schola and Unreal Engine
Train a robot arm with reinforcement learning in AMD Schola using Unreal® Engine, progressively increasing task complexity to adapt to changing conditions.

AMD Schola is a library for developing reinforcement learning (RL) agents in Unreal® Engine, and training with your favorite python-based RL frameworks: Gym, RLlib and Stable Baselines 3.
AMD Schola v2 introduces a powerful and flexible architecture that decouples the inference process into components for maximum flexibility and reusability. This modular design allows you to mix and match different policies, stepping strategies, and agent implementations to suit your specific needs.
Key Components:
Agent Interface - Define an agent that takes actions and makes observations.
UInferenceComponent - Add inference to any actor.AInferencePawn - Standalone pawn-based agents.AInferenceController - AI controller pattern for complex behaviors.Policy Interface - Plug in different inference backends, to turn observations into actions.
UNNEPolicy - Native ONNX inference with Unreal Engine’s Neural Network Engine.UBlueprintPolicy - Custom Blueprint-based decision making.Stepper Objects - Control inference execution patterns by coordinating agents and policies.
SimpleStepper - Synchronous, straightforward inference.PipelinedStepper - Overlap inference with simulation for better throughput.This architecture means you can easily switch between inference backends, optimize performance characteristics, and compose behaviors without rewriting your agent logic. Whether you’re prototyping with Blueprints or deploying production-ready neural networks, the same agent interface works seamlessly with your chosen policy and execution strategy.
AMD Schola v2 introduces native support for the Minari dataset format, the standard for offline RL and imitation learning datasets. Minari provides a unified interface for storing and loading trajectory data, making it easier to share demonstrations and datasets across different projects and research communities.
One of the most powerful improvements in AMD Schola v2 is robust support for agents being spawned and deleted mid-episode. Previous versions required a static set of agents throughout an episode, or a predefined spawning function to spawn agents but v2 can now handle dynamic populations seamlessly.
This enables realistic scenarios like:
The system lets you manage lifecycles the way you want, simply mark the agents as terminated when they die, or start reporting observations when they spawn. This makes it much easier to build realistic, dynamic environments that mirror actual game scenarios.
Training from the command line is now more intuitive than ever:
# Stable Baselines 3schola sb3 train ppo ...
# Ray RLlibschola rllib train ppo ...
# Utilitiesschola compile-protoschola build-docsThe new CLI built with cyclopts provides better error messages, auto-completion support, and a more consistent interface across different RL frameworks.
Working in Unreal Engine Blueprints is smoother than ever:
AMD Schola v2 has been updated to support the latest versions of all major RL frameworks and libraries:
These updates ensure you can leverage the latest features, bug fixes, and performance improvements from the RL ecosystem while training your agents in Unreal Engine.
Schola provides tools for connecting and controlling agents with ONNX models inside Unreal Engine, allowing for inference with or without Python.
Schola exposes simple interfaces in Unreal Engine for the user to implement, allowing you to quickly build and develop reinforcement learning environments.
Environments in Schola are modular so you can quickly design new agents from existing components, such as sensors and actuators.
Train multiple agents to compete against each other at the same time using RLlib and multi-agent environments built with Schola.
Run multiple copies of your environment within the same Unreal Engine process to accelerate training.
Run training without rendering to significantly improve training throughput.
The Basic environment features an agent that can move in the X-dimension and receives a small reward for going five steps in one direction and a bigger reward for going in the opposite direction.
The MazeSolver environment features a static maze that the agent learns to solve as fast as possible. The agent observers the environment using raycasts, moves by teleporting in 2 dimensions and is given a reward for getting closer to the goal.
The 3DBall environment features an agent that is trying to balance a ball on-top of itself. The agent can rotate itself and receives a reward every step until the ball falls.
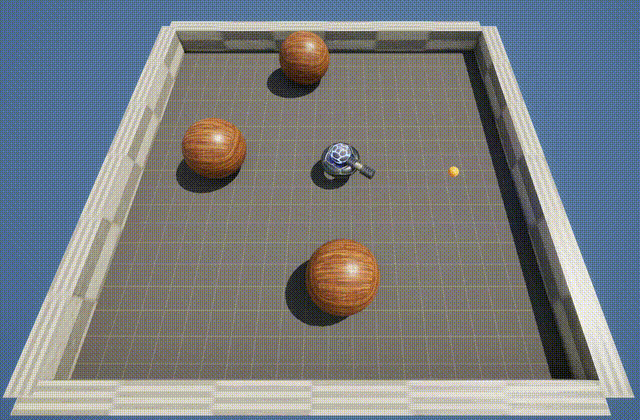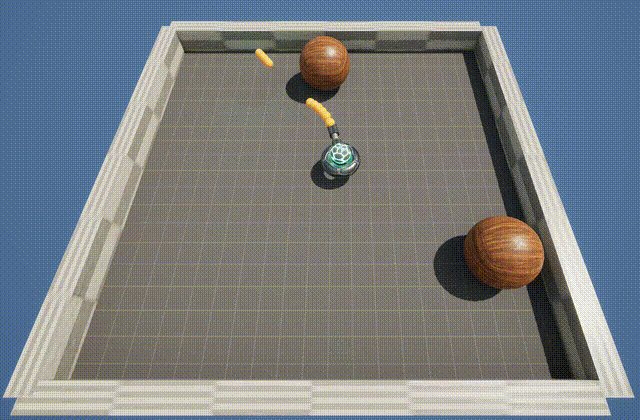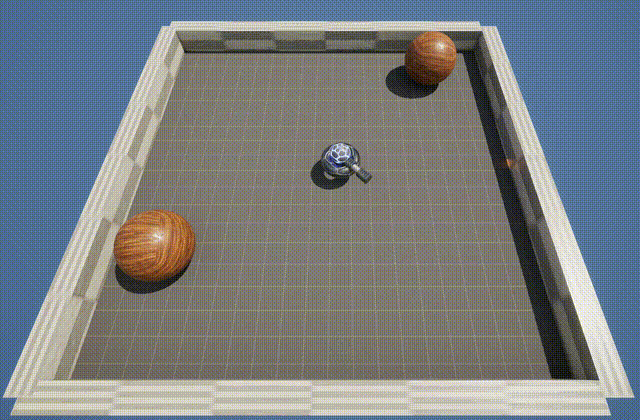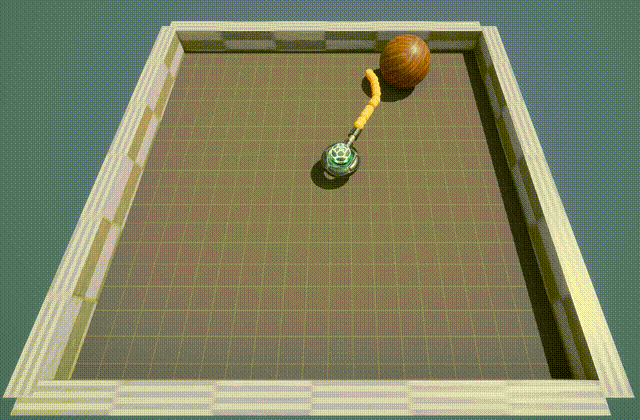
The BallShooter environment features a rotating turret that learns to aim and shoot at randomly moving targets. The agent can rotate in either direction, and detects the targets by using a cone shaped ray-cast.
The Pong environment features two agents playing a collaborative game of pong. The agents receive a reward every step as long as the ball has not hit the wall behind either agent. The game ends when the ball hits the wall behind either agent.
The Tag environment features a 3v1 game of tag, where one agent(the runner) has to run away from the other agents which are trying to collide with it. The agents move using forward, left and right movement input, and observe the environment with a combination of ray-casts and global position data.
The RaceTrack environment features a car implemented with Chaos Vehicles, that learns to follow a race track. The agent controls the throttle, break and steering of the car, and can see it’s velocity and position relative to the center of the track.

Unreal® is a trademark or registered trademark of Epic Games, Inc. in the United States of America and elsewhere.
“Python” is a trademark or registered trademark of the Python Software Foundation.