The all new Radeon™ gaming architecture powering “Navi”.
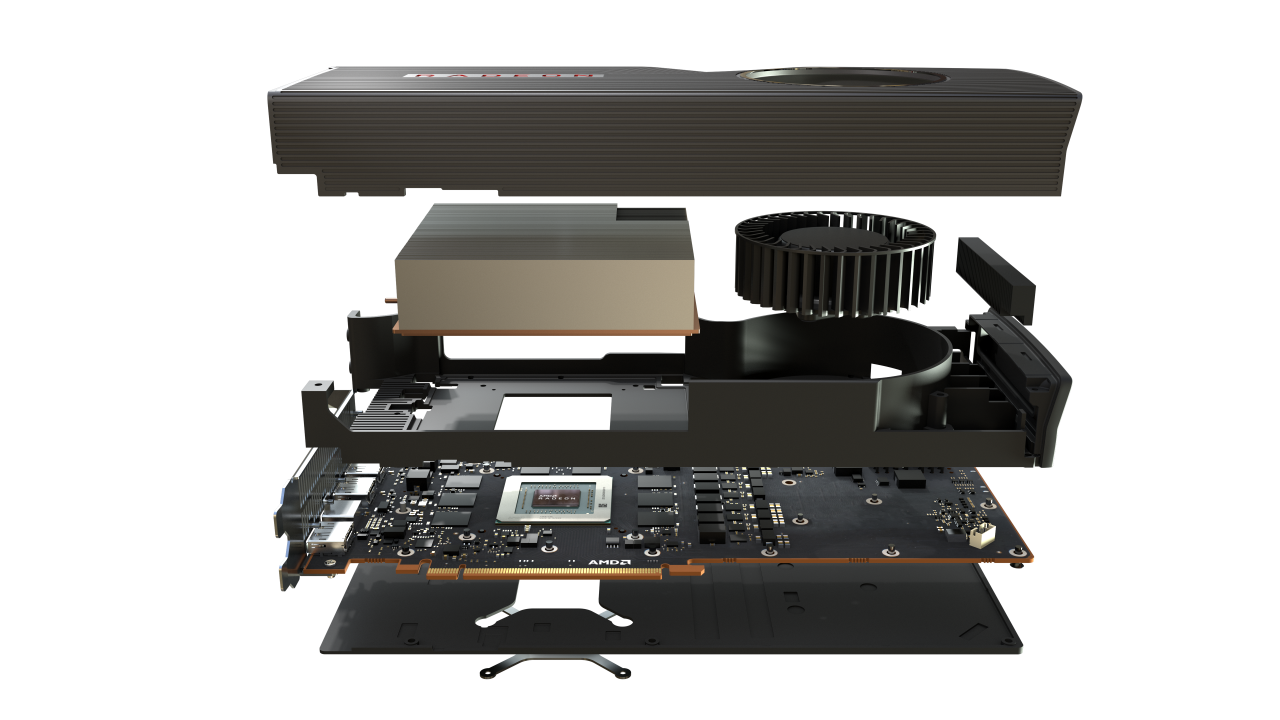
With RDNA, AMD has revisited almost every block in the hardware with a drive, tenacity and focus to make RDNA our best ever architecture for graphics and low latency compute.
Among a myriad of changes, RDNA introduces a lower-latency, higher effective IPC shader core and a new cache hierarchy.
Download the RDNA architecture presentation for developersRead the RDNA Performance Guide

RDNA Documentation
The document is intended for programmers writing application and system software, including operating systems, compilers, loaders, linkers, device drivers, and system utilities.
It assumes that programmers are writing compute-intensive parallel applications and assumes an understanding of requisite programming practices.
The new RDNA architecture is optimized for efficiency and programmability while offering backwards compatibility with the GCN architecture. It still uses the same seven basic instruction types: scalar compute, scalar memory, vector compute, vector memory, branches, export, and messages. However, the new architecture fundamentally reorganizes the data flow within the processor, boosting performance and improving efficiency.
Find out more by downloading the RDNA Whitepaper
Related software




Related news and technical articles




Related videos